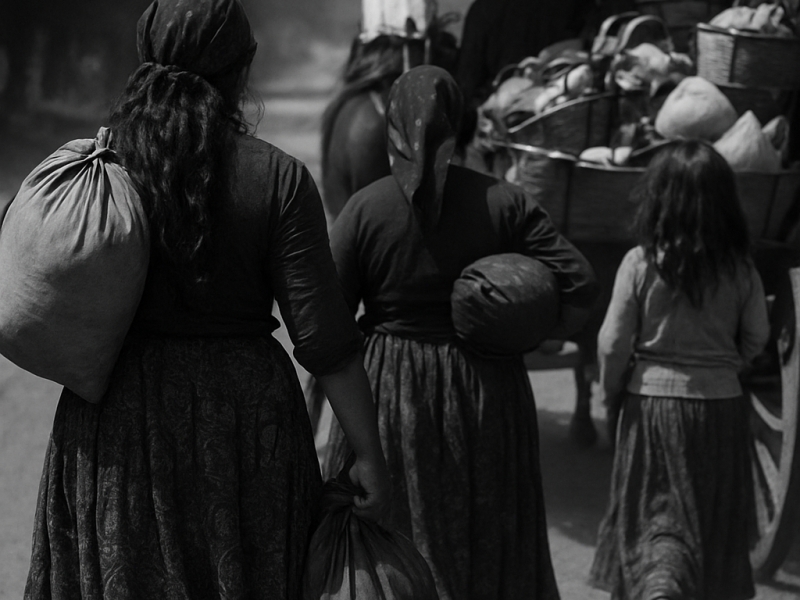Focus ROMI.HR
/Approximately 1000 years ago, Roma, which had left India and settled in various countries, also migrated to Azerbaijan. The arrival of the Roma to Azerbaijan, where they managed to preserve and maintain their traditions, happened for various reasons.
The information about the arrival and settlement of Roma in Azerbaijan and their overall origin is limited. Kerope Patkanov, a Russian ethnographer of Armenian origin who lived in the 19th century, noted that there was little discussion about the language and existence of the Roma people in Azerbaijan.However, we will explore this topic as much as possible.
It is believed that the Romani population in Azerbaijan comes from the Dom branch. Doms are ethnic groups descended from Doms from the Indian peninsula, who migrated to the Middle East, North Africa, and Eastern Anatolia Region in the 3rd-10th centuries. The Doms are sometimes identified with the Roma and Lom, other ethnic groups who migrated from India. But they left India at different times and in different directions. It is also known that the Domari language has a different origin than the Romani language.
Zafer Kemal oglu Kilincher mentioned that Roma people from Azerbaijan belong to the "dom" originating from Iran. Patkanov suggested that the Roma people in the South Caucasus, the Roma in Europe, the Bosha in Asia Minor, and the Dom in Iran were the same ethnic group that had split into several groups for historical reasons. The Roma in Azerbaijan were related to the Roma living around the city of Tabriz in northwestern Iran, the Suzmanis in northwestern Iran, and the Roma in southeastern Turkey (called Qereçî in Kurdish and Karaçi in Turkish). According to Jean-Marie Chopin, Roma in Azerbaijani are descendants of Romani migrants from Central Asia in the Middle Ages. In 1944, Vasili Yan suggested a differentiation between Roma from Azerbaijani and Dom from Iran (sometimes referred to as Garachi) based on their origins. Generally, the roots of the Roma people in Azerbaijan are believed to come from the population that migrated from India to Iran. According to Kılıncher, the Roma people living in Azerbaijan migrated from India to Iran and then moved to Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Kazakhstan.
Ethnographer Nargiz Guliyeva states that the arrival of Roma people to Azerbaijan occurred through migration from the Karachi city, the province of Pakistan to Quba and Nukha districts of Azerbaijan in the 13th century. The word "qaraçı" used in Azerbaijan is also associated with that region. Also, this word is linked to the Azerbaijani term "çığırqan" (meaning "squealing"), which was related to the trading style of the Roma people in the past. According to the words of a Roma from Shamakhi district of Azerbaijan, another etymology of this word is connected to the “Gara” village in in Srikakulam district in India.
Additionally, the mass migration of the Roma people to Azerbaijani territories is associated with the Safavid Empire's Shah Abbas I. In the XVII century he utilized migration policies to suppress local uprisings, and the number of settled down Roma people exceeded 2,000. The Roma people, mainly settled in the Balakan district of Azerbaijan, were sometimes referred to as Kurds by the local population due to their Persian-speaking language. Because Kurds in Iran are mostly speak in Kurdish, Gorani and Persian. Another reason why Roma in Azerbaijan call themselves Persians and Kurds is that they first came to Iran and adapted to the population, their language, and religion. Therefore, the ethnographer Emil Karimov assumes that when this nation came from Iran, they began to present themselves as Kurds, not as Roma or Garachi. Khachmaz district in Azerbaijan is considered to be one the first places of settlement for Roma, and the area where they settled is still called Garachi village. Although at present they live more compactly in Khudat village of Khachmaz.
There is no specific information about the Roma life in Azerbaijan during the reign of the Afshar empire, which arose after the fall of the Safavids, and later the Azerbaijani khanates and Gajars in the 19th century.
It is estimated that the largest migration of Roma to Azerbaijan took place in groups at the end of the 19th century, as in the 19th and 20th centuries they came to Azerbaijan to visit the Zoroastrian temples located in the country. Zoroastrianism, spread in Iran in the 7th century BC, is considered one of the oldest religions in the world. It was also expected that this religion, which was widespread in India, would be accepted by Roma. Over the year, Roma, like the majority of Azerbaijani Turks, have been attached to the Shiite branch of Islam.
In 1887, Kerope Patkanov noted that during the time of the Russian Empire there were 2,399 Roma people living in the South Caucasus. Patkanov's analysis of the Roma language (based on 101 expressions) presented that despite being of ‘’Indo-Aryan” (or Indic languages) origin, the Roma people in Azerbaijan did not have mutual understanding with the Roma or Dom dialects of the Balkans, Russia, or the Middle East. Additionally, Patkanov observed that the Roma people spoke Azerbaijani as a second or third language and sometimes spoke Tat language.Their main occupation was the production of household items such as baskets, sieves, and chewing gum, which were made by men and sold by women in neighboring towns. Patkanov lists fortune-telling and cattle rustling among other sources of income. Nomadic Roma groups taught tricks to animals and performed together with them in front of the public, engaged in traveling musicians and dancers. Patkanov noted that Tatar weddings were held with Roma musicians called "hoggabaz", singers called "chensh" and dancers called "mutrif".
In conclusion, the Roma people in Azerbaijan have a history shaped by migration and cultural blending. From their origins in the Dom branch to later migrations influenced by historical events, the Roma have played a significant role in Azerbaijani society.
 Back to Focus
Back to Focus